What Manorexia Symptoms Should You Watch for in 2026?
Key Highlights
- Manorexia refers to anorexia nervosa in men, driven by distorted body image and societal pressures to attain a muscular physique.
- Common symptoms include emotional distress, excessive exercise, preoccupation with body image, and significant weight loss.
- The disorder is influenced by biological, psychological, and cultural factors, contributing to its complexity.
- Medical complications such as cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and hormonal issues can arise from untreated manorexia.
- A multidisciplinary approach involving therapy, nutritional counseling, and medical support is essential for recovery.
- Early identification of manorexia symptoms is crucial to prevent the escalation of the disorder and to address underlying emotional and physical issues.
Manorexia, a term used to describe anorexia nervosa in men, is becoming an increasingly recognized mental health issue. Despite its growing awareness, many men still struggle with this condition due to societal stigma and a lack of support systems. Left unaddressed, the symptoms can lead to severe physical and emotional consequences.
The challenge lies in identifying the early warning signs of manorexia. Men often hide their struggles, focusing on muscle mass and physical appearance rather than weight loss, making it difficult to spot the disorder. Understanding these unique symptoms is essential to preventing the escalation of this disorder.
This blog aims to highlight the common symptoms of manorexia, explore its causes, and provide insight into its treatment options. By raising awareness, we hope to guide individuals toward seeking the help they need for recovery.
What is Manorexia?
When most people think of eating disorders, they often envision women struggling with body image issues. However, eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa, can affect individuals of all genders, ages, and backgrounds. Manorexia refers specifically to anorexia nervosa in men.
The manorexia definition highlights how this condition is often unrecognized and goes undiagnosed, largely due to societal stigmas surrounding men and mental health. In fact, many men suffering from manorexia may still appear strong or fit, especially in cultures that emphasize muscularity and low body fat as ideals of masculinity. Hence, recognizing the signs and symptoms of manorexia is crucial for early intervention and support.
What are The 10 Common Manorexia Symptoms?
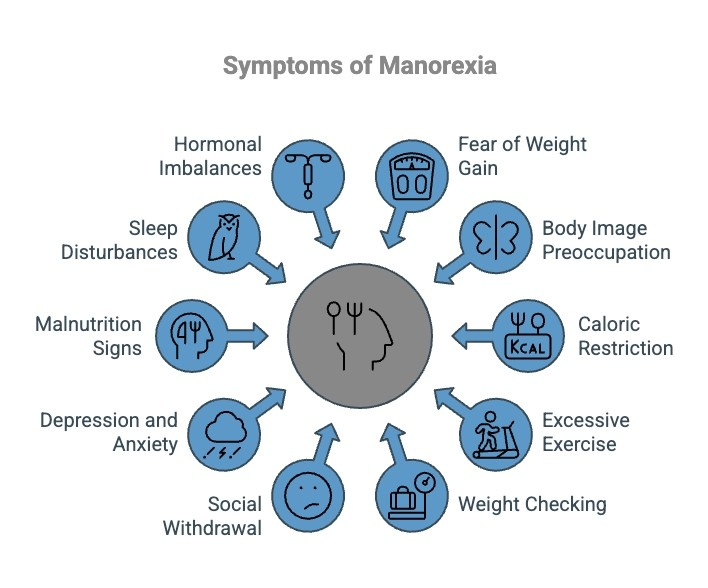
Manorexia is frequently overlooked because it is typically linked to women. However, manorexia cases in men are becoming more prevalent, marked by an intense fear of weight gain and a preoccupation with attaining a muscular, lean physique. This disorder is often hidden due to societal expectations of masculinity, making early identification of symptoms essential for effective intervention and treatment.
Here are some of the key signs to look out for:
1) Intense Fear of Weight Gain
An irrational fear of gaining weight is a hallmark symptom of manorexia. This overwhelming fear persists even when the individual is already underweight or has a healthy weight. Here are some of the ways the intense fear of weight gain manifests in men with manorexia:
- Obsession with maintaining a low body fat percentage or lean physique.
- Constant worry about even a slight increase in weight, leading to drastic measures.
- Fear of eating certain foods due to their potential to cause weight gain.
- Engaging in excessive exercise to “burn off” any perceived calories consumed.
2) Preoccupation with Body Image
Men with manorexia develop a distorted perception of their body, often fixating on muscle definition and body fat percentage. This leads to dissatisfaction despite being underweight. Here are the signs of how a distorted body image plays a significant role in manorexia:
- Seeing oneself as overweight, even with a low body fat percentage.
- Obsessive thoughts about body size, shape, and muscle tone.
- Constant comparisons with others in terms of appearance.
- Overemphasis on achieving a “perfect” physique, particularly a muscular build.
Learn how the media influences body image and self-esteem. Check out these 12 Media Self-Esteem Test Questions to understand how media impacts perceptions of body image and mental health.
3) Extreme Caloric Restriction
Individuals with manorexia severely limit their food intake to control weight and achieve the desired body. This restriction can result in malnutrition and health complications. Here are some behaviors associated with extreme caloric restriction in manorexia:
- Skipping meals or eating extremely small portions.
- Rigid food rules, such as avoiding certain food groups or types.
- Fear of eating “unhealthy” foods, leading to strict dieting.
- Obsession with calorie counting and limiting intake below daily nutritional needs.
4) Excessive Exercise
Excessive and often compulsive exercise is used to control weight and enhance muscle definition. This behavior can take a physical toll and may lead to injuries. Here are the behaviors associated with excessive exercise seen in individuals with manorexia:
- Spending hours at the gym, engaging in intense weightlifting, or cardio.
- Feeling anxious or guilty if a workout is missed.
- Exercising even when tired, sick, or injured, often pushing the body to extremes.
- Using exercise to “make up” for eating or to burn off calories.
5) Obsessive Weight Checking
Frequent checking of weight on a scale is a common behavior in manorexia. The number on the scale becomes a constant source of anxiety and validation. Here are the ways obsessive weight checking impacts the individual:
- Weighing oneself multiple times a day, often obsessively.
- Feelings of anxiety or panic if the weight increases, even slightly.
- Emotional distress is tied to fluctuations in weight, no matter how small.
- Weight checks are becoming a compulsive routine that dictates mood and behavior.
6) Social Withdrawal and Isolation
Men with manorexia often withdraw from social situations to avoid eating or being judged. This isolation can exacerbate mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Here are the ways manorexia causes social withdrawal and isolation:
- Avoiding social events, particularly those involving food or eating.
- Feeling uncomfortable eating in front of others, leading to isolation.
- Fear of being criticized for body size or food choices during social gatherings.
- Reduced social interaction due to shame or guilt surrounding eating habits.
7) Depression and Anxiety
The constant pressure to control body image and fear of weight gain can lead to significant mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety. Here are the common signs of depression and anxiety associated with manorexia:
- Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or worthlessness.
- Increased anxiety, especially around eating, weight, or body image.
- Emotional instability, including irritability or mood swings.
- Struggling to cope with stress due to the obsession with the body and food.
8) Physical Signs of Malnutrition
Malnutrition due to extreme caloric restriction causes various physical changes. These can include visible signs like dry skin and hair loss, as well as fatigue and weakness. Here are the physical signs of malnutrition commonly seen in manorexia:
- Dry, flaky skin and thinning or brittle hair.
- Extreme fatigue and weakness, making daily tasks difficult.
- Muscle wasting or loss of muscle mass due to insufficient nutrients.
- Dizziness, fainting, or lightheadedness caused by inadequate nutrition.
9) Insomnia and Sleep Disturbances
The mental and physical strain of manorexia often leads to trouble sleeping. This can worsen fatigue and impact overall well-being. Here are some ways insomnia and sleep disturbances affect men with manorexia:
- Difficulty falling or staying asleep due to anxiety or stress.
- Restlessness during the night, with frequent wake-ups.
- Racing thoughts about food, weight, or exercise preventing relaxation.
- Feeling tired or unable to function during the day due to poor sleep quality.
10) Hormonal Imbalances
Malnutrition and extreme exercise can disrupt hormonal function, leading to changes in mood, libido, and physical health, such as muscle loss or infertility. Here are the signs that hormonal imbalances can lead to further complications:
- Decreased testosterone levels, leading to reduced libido and erectile dysfunction.
- Disruption of reproductive hormones, causing irregular or absent menstrual cycles (in men, this may affect sperm count).
- Decreased bone density, making bones weaker and more prone to fractures.
- Muscle loss and fatigue due to insufficient nutritional support for hormone production.
These symptoms highlight the complex nature of manorexia, affecting both the mind and body. Recognizing these signs is crucial for timely intervention and treatment.
What Causes Manorexia?
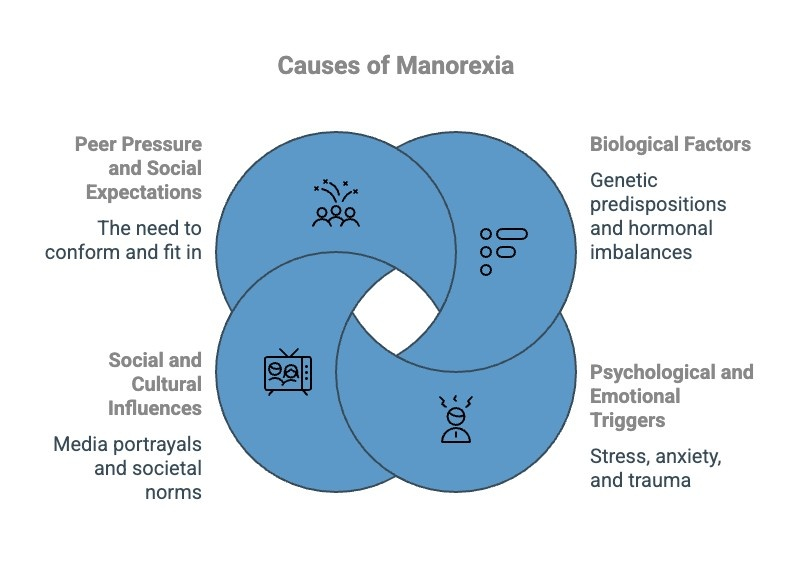
The development of manorexia is influenced by a combination of factors, both internal and external. Understanding what causes it and identifying who is most at risk is crucial for prevention and early intervention.
Let’s delve into the key causes and risk factors that contribute to this serious disorder:
1) Biological Factors Contributing to Manorexia
Genetic predispositions, hormonal imbalances, and brain chemistry can play a significant role in the development of manorexia. Research suggests that individuals with a family history of eating disorders may be more likely to develop this condition.
2) Psychological and Emotional Triggers
Manorexia often stems from emotional and psychological factors, including low self-esteem, trauma, and a distorted body image. The pressure to meet societal standards of masculinity can also contribute to the development of this disorder.
3) Social and Cultural Influences on Manorexia
Cultural expectations of the “ideal” male body can fuel unhealthy behaviors and lead to manorexia. Media portrayals of muscular and lean men can create unrealistic standards, pressuring individuals to conform and neglect their physical and mental health.
4) Peer Pressure and Social Expectations
Peer pressure, particularly in environments such as sports or bodybuilding, can increase the risk of developing manorexia. Men may feel compelled to attain a certain physique to gain social acceptance or to meet competitive standards.
By recognizing the underlying causes and at-risk groups, we can better understand manorexia and take proactive steps toward addressing it, ensuring individuals receive the help they need for recovery and well-being.
Who Is Most At Risk for Manorexia?
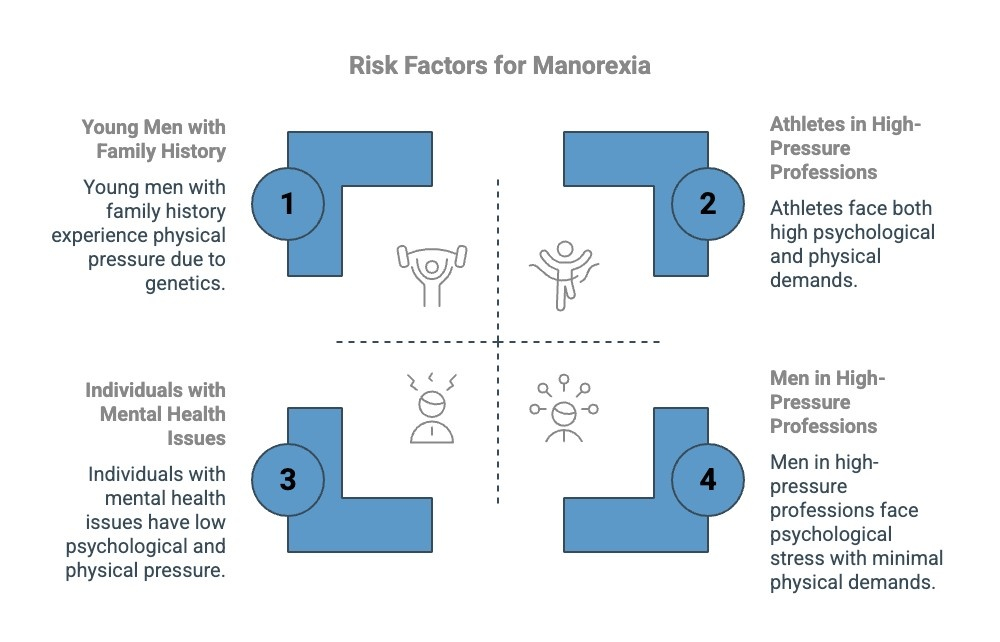
While manorexia can affect anyone, certain individuals are more vulnerable due to various factors. These include:
- Young Men: Adolescents and young adults, particularly those in their teens and early twenties, are at a higher risk due to body image concerns and peer pressures.
- Athletes and Fitness Enthusiasts: Men involved in sports or bodybuilding, especially those focused on maintaining a specific physique, may face greater pressure to conform to societal ideals of masculinity.
- Individuals with a History of Mental Health Issues: Those who have struggled with anxiety, depression, or other mental health conditions are more likely to develop disordered eating habits like manorexia.
- Men in High-Pressure Professions: Jobs or lifestyles that emphasize physical appearance or performance, such as modeling or acting, can increase the risk for developing manorexia.
- Those with Family History of Eating Disorders: A genetic predisposition or a family history of eating disorders may make individuals more susceptible to developing manorexia.
Recognizing these risk factors allows for more targeted and proactive support. If you or someone you know is struggling with anxiety or depression, it’s important to seek professional help. For more information on managing these mental health challenges, consider reading:
What Are the 5 Medical Complications Manorexia Disease Can Cause?
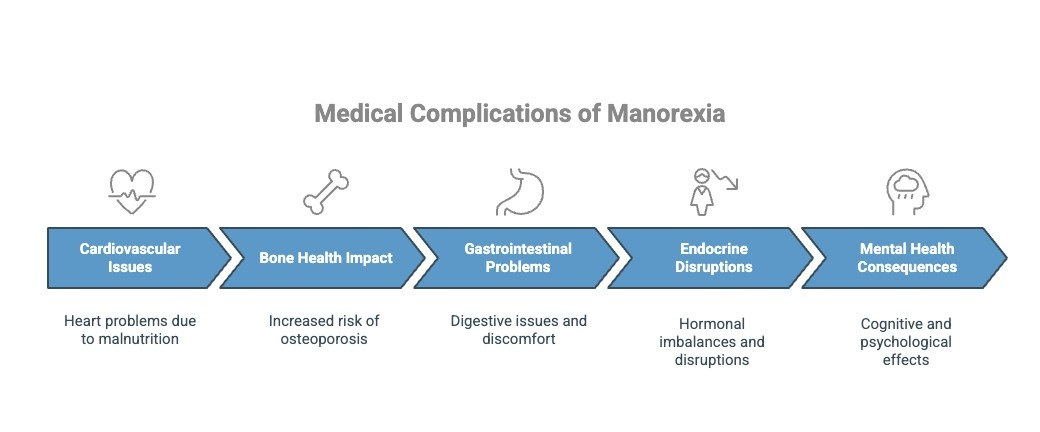
Manorexia can have far-reaching consequences that extend beyond its psychological effects. The physical toll on the body can be severe, leading to a variety of medical complications. Understanding these potential risks is critical for early intervention and treatment.
Let’s explore some of the most significant medical complications associated with manorexia:
1) Cardiovascular Issues Linked to Manorexia
Manorexia can lead to severe heart complications, including low blood pressure, slow heart rate, and an increased risk of heart failure. These issues arise from malnutrition and the body’s inability to function properly without adequate nutrition.
2) Impact on Bone Health and Risk of Osteoporosis
The lack of proper nutrition in individuals with manorexia can lead to weakened bones, making them more prone to fractures and conditions like osteoporosis. This is particularly concerning in younger men, as it can affect bone development.
3) Gastrointestinal Problems Associated with Manorexia
Malnutrition can cause severe gastrointestinal issues, such as bloating, constipation, and delayed gastric emptying. In some cases, individuals may experience digestive issues that can lead to long-term problems if not addressed.
Learn more about the Gut-Brain Connection.
4) Endocrine Disruptions and Hormonal Imbalance
Manorexia can cause disruptions in hormone levels, leading to issues like infertility, and low testosterone. These hormonal imbalances can have lasting effects on overall health.
5) Mental Health and Cognitive Consequences
Beyond physical health, manorexia can also take a toll on mental health. Anxiety, depression, and cognitive impairments, such as difficulty concentrating and memory issues, are common in those suffering from the disorder.
Recognizing the medical complications of manorexia is essential for early intervention and preventing long-term health consequences. At Total Life Counseling (TLC), we specialize in providing the support needed for recovery. If you or someone you know is struggling, contact TLC today to begin the journey toward healing and improved well-being.
What Does Effective Manorexia Treatment Look Like?
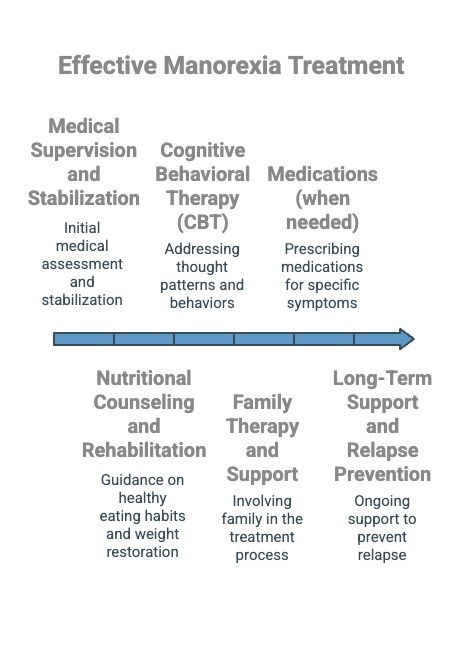
Effective treatment for manorexia involves a multidisciplinary approach, combining medical, psychological, and nutritional support to address both the physical and mental aspects of the disorder. Here are some key components:
- Medical Supervision and Stabilization: The first step in treatment often involves medical monitoring to address any life-threatening conditions, such as malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, and organ dysfunction. Ensuring the individual’s physical health is stabilized is critical before proceeding to other treatments.
- Nutritional Counseling and Rehabilitation: A registered dietitian or nutritionist works closely with the individual to develop a healthy eating plan, aiming to restore proper nutrition, address disordered eating behaviors, and promote a balanced relationship with food.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): CBT is one of the most effective therapeutic approaches for treating manorexia. It helps individuals identify and change harmful thought patterns related to body image, food, and self-worth, ultimately working to reduce the drive for extreme weight loss.
- Family Therapy and Support: Involving family members in the treatment process can help address family dynamics that may contribute to or perpetuate the disorder. Family therapy fosters communication and provides a support system for recovery.
- Medications (when needed): While no specific medications are approved to treat manorexia, psychiatric medications like antidepressants or anti-anxiety drugs may be prescribed to help manage co-occurring conditions such as depression or anxiety.
- Long-Term Support and Relapse Prevention: Recovery from manorexia is an ongoing process. Long-term treatment may include continued therapy, support groups, and lifestyle adjustments to help maintain progress and prevent relapse.
With the right combination of medical, psychological, and nutritional support, individuals can overcome manorexia and begin the path toward recovery. Early intervention and a tailored treatment plan are vital in achieving long-term success and improved well-being.
Are You Struggling with Manorexia? Get Professional Help at Total Life Counseling
If you or someone you know is struggling with manorexia, seeking professional help is the first step toward recovery. At Total Life Counseling, we specialize in providing comprehensive care for individuals facing eating disorders, including manorexia. Our multidisciplinary approach combines medical, psychological, and nutritional support to ensure that each individual receives the care they need to recover fully.
Whether it’s through individual therapy, family support, or tailored nutritional counseling, our team is here to guide you through every step of the healing process. We understand the challenges of manorexia, and we’re committed to providing a compassionate and non-judgmental environment for recovery.
Don’t wait, help is available! Contact us today to schedule a consultation and start the journey toward a healthier, more balanced life. Early intervention is key to recovery, and with the right support, you can regain control over your health and well-being.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs and symptoms of manorexia is the first step toward addressing the disorder. If you or someone you know is struggling, it’s important to seek help as soon as possible. Early intervention can make a significant difference in recovery outcomes. Surround yourself with the right support, whether through professional treatment, support groups, or trusted friends and family. With the right approach, recovery is possible, and regaining a healthier relationship with food and body image is achievable.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can physical symptoms alone indicate manorexia in men?
Physical symptoms like low body weight or BMI are red flags for manorexia, but they don’t capture the full picture. Manorexia is a psychological eating disorder requiring behavioral and emotional signs for diagnosis.
Is muscle dysmorphia considered part of manorexia disease?
Muscle dysmorphia and manorexia are related but separate disorders. While manorexia focuses on thinness, muscle dysmorphia centers on insufficient muscularity. Both are linked by distorted body image and may co-occur, leading to an eating disorder.
What are the first steps in seeking manorexia treatment?
The first step in getting eating disorder treatment is reaching out for professional medical advice. Contacting a doctor or mental health services can begin the process of getting a diagnosis and creating a treatment plan. Organizations like the National Eating Disorders Association offer resources and can connect you with specialists who can help.
Are the signs of manorexia different from those in women with anorexia?
To define manorexia, it refers to anorexia nervosa in men. While the core symptoms of anorexia and manorexia are similar, men may hide their condition more due to stigma. Men may also focus more on muscle tone and physical appearance, while women often focus on weight loss.
How can you distinguish manorexia symptoms from general anorexia symptoms?
Manorexia symptoms are similar to anorexia but may include a greater emphasis on muscle definition and body size. Men may also engage in excessive exercise or bodybuilding. Recognizing these signs of an eating disorder is crucial for early intervention.
What early warning signs might indicate that a man is developing manorexia?
Early warning signs of manorexia include obsessive thoughts about body image, extreme exercise routines, restrictive eating, rapid weight loss, and excessive focus on building muscle. Mood swings, anxiety, and social withdrawal may also indicate developing manorexia.
What physical changes might suggest a man is struggling with manorexia?
Physical changes in manorexia may include muscle loss, low body fat, fatigue, dry skin, and brittle hair. These are often linked to food restriction, body dissatisfaction, and restrictive food intake disorder, impacting overall health.
Filed in: Anorexia, Anxiety, Depression, Eating Disorders, Jada Jackson, Orlando, Updates
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Total Life Counseling Center consists of Licensed Counselors, masters level therapists, Español counselors, Licensed Mental Health Counselors, business coaches, and image enhancement coaches who provide counseling for emotional, mental, physical and spiritual care including marriage, individual, family, substance abuse and more. TLC’s family, trauma and marriage experts have been interviewed on National and Local TV/Radio over 200 times for their expert advice on Fox News, OWN, WETV, ABC’s Medical Minute and more. Our skilled counselors are relational, approachable and specialists providing therapy services in the Central Florida area including: Orlando, Winter Park, MetroWest, Windermere, Dr. Phillips, East Orlando, Lake Mary, and Clermont, Boca Raton Florida, and Dallas, TX.






Losing not loosing (used twice). Otherwise I enjoyed your article.